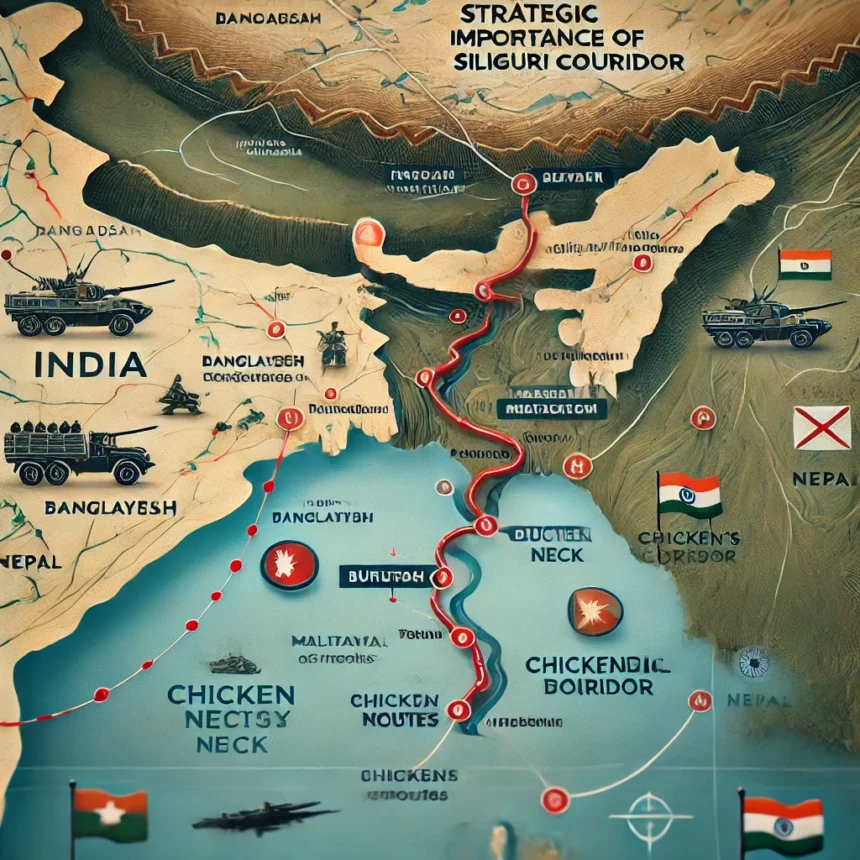
The Siliguri Corridor, often termed the “Chicken’s Neck,” is a critical geographical bottleneck for India, connecting the northeastern states to the rest of the country. As Bangladesh grapples with political turmoil, there are growing calls within strategic circles to re-evaluate India’s stance on the Siliguri Corridor. This article delves into the significance of the corridor, the potential risks and rewards of expansion, and the broader geopolitical implications.
1. Importance of the Siliguri Corridor:
Geography and Strategic Significance:
- Vital Connection: The Siliguri Corridor is a narrow stretch of land, approximately 22 kilometers wide, that connects India’s northeastern states to the mainland. It is flanked by Nepal and Bhutan to the north and Bangladesh to the south, with China’s Chumbi Valley lying just beyond Bhutan.
- Strategic Routes: Key highways, including NH10 and NH27, traverse this corridor, facilitating military and civilian logistics. The corridor is not only a lifeline for the northeastern states but also a strategic point for the Indian military to maintain connectivity and rapid deployment capabilities.
- Vulnerability: The proximity of neighboring countries makes the corridor highly vulnerable to potential blockades or disruptions. In the event of a conflict, particularly with China, this narrow strip could be a significant chokepoint.
Military Presence and Challenges:
- Defensive Posture: India has a robust military presence in the region, including the Indian Army, Border Security Force (BSF), and Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP). These forces are tasked with safeguarding the corridor against potential threats, including cross-border insurgencies and Chinese military activities.
- Strategic Concerns: The narrowness of the corridor raises concerns about its defensibility, especially in a two-front conflict involving China and Pakistan. The terrain’s complexity further complicates military logistics and rapid reinforcement.
2. The Political Crisis in Bangladesh:
Recent Developments:
- Political Instability: Bangladesh is currently experiencing significant political instability, exacerbated by the departure of Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina and the rise of an interim government. The situation is marked by widespread unrest, attacks on minorities, and a general breakdown of law and order.
- Impact on India: The turmoil in Bangladesh has heightened security concerns for India, particularly along the shared border. There is an increased risk of cross-border insurgency, illegal immigration, and destabilization of border regions.
Opportunity or Risk?
- Radical View:
- Expansion of the Corridor: Some strategic analysts argue that India should capitalize on Bangladesh’s political vacuum to secure and potentially expand the Siliguri Corridor. This could involve annexing additional territory from Bangladesh to widen the corridor, thereby enhancing India’s strategic depth and reducing vulnerability.
- Geopolitical Risks: However, such a move would likely provoke significant international backlash. It could strain India’s diplomatic relations with Bangladesh, draw criticism from the international community, and potentially invite economic sanctions or military confrontations.
- Cautious View:
- Diplomatic Restraint: Others advocate for a more cautious approach, emphasizing the importance of maintaining regional stability and avoiding aggressive actions. They argue that India should focus on strengthening diplomatic ties with Bangladesh, working towards mutually beneficial agreements that enhance security and connectivity without resorting to territorial expansion.
- Alternative Routes: Developing alternative logistics routes, such as through Myanmar or via improved infrastructure in the northeastern states, could reduce India’s dependency on the Siliguri Corridor, making it less of a strategic vulnerability.
3. Alternative Strategies:
Develop Infrastructure in Northeastern India:
- Reducing Dependency: One of the most viable alternatives to expanding the Siliguri Corridor is to develop better infrastructure within the northeastern states. This includes constructing new highways, railways, and airstrips that bypass the vulnerable corridor.
- Economic Integration: Enhancing connectivity within the northeastern states could also promote economic integration with the rest of India, reducing the strategic need for the corridor while boosting local economies.
Strengthen Ties with Bangladesh:
- Leveraging Diplomatic Channels: India could leverage Bangladesh’s need for economic stability to negotiate access through their territory. This could involve agreements that allow India to use Bangladeshi territory for transit, thereby creating alternative routes to the northeastern states.
- Counterbalancing Chinese Influence: Strengthening ties with Bangladesh could also serve as a counterbalance to China’s growing influence in the region. By fostering closer economic and security cooperation, India could reduce the strategic threats posed by both Bangladesh’s instability and China’s ambitions.
Conclusion:
India faces a complex and delicate situation regarding the Siliguri Corridor. While expanding the corridor in response to Bangladesh’s political crisis may offer short-term strategic gains, the long-term consequences could be detrimental to India’s regional and international standing. A more measured approach, focusing on diplomatic engagement and infrastructure development, may offer a more sustainable solution to the challenges posed by the Siliguri Corridor.
What are your thoughts on India’s strategic options regarding the Siliguri Corridor? Should India take a bold stance or opt for a more cautious approach? Share your insights and join the discussion in the comments below!